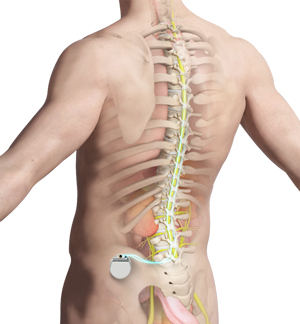
Spinal Cord Stimulator
Back and leg pain often have causes which either improve on their own or which the surgeon can correct. Sometimes there is no easily correctable cause of the pain.
Among other things, scar tissue around the nerves or chronic inflammation of the nerves such as arachnoiditis may cause leg and back pain. When the neurosurgeon feels that open surgery to decompress the nerves is unlikely to help the pain, an operation to implant a spinal cord stimulator may be very beneficial for the patient.
For reasons not completely understood, the stimulator sends electrical impulses to the areas of the spinal cord causing the pain and interferes with the transmission of pain signals to the brain. It blocks the brain's ability to sense pain in the stimulated areas, thus relieving pain without the side effects that medications can cause. The electrical impulses can be targeted to specific locations and, as pain changes or improves, stimulation can be adjusted as necessary.
Before implanting a permanent stimulator, the patient will undergo a trial stimulation period to see if the stimulation helps with their pain. If it does, a permanent stimulator may be implanted. A battery pack will also be implanted to provide charge to the stimulator.
Procedure
There are several ways of implanting the stimulator. The initial implantation of the trial is generally done with the patient awake so that it can be determined in the operating room if the stimulator is covering the appropriate spot of the spinal cord in order to give the patient pain relief.
Either a paddle lead is placed over the spinal cord through a small open incision and removal of lamina, or a percutaneous insertion of a lead is performed through the skin. The permanent implant will be fixed several days later if the patient achieves good pain relief with the trial stimulator.
Post-operative Care
Patients are generally discharged on the same day or the following day of the procedure. They should keep the wounds very clean and dry.
Risks
Risks for the procedure are low. Potential risks include bleeding, infection, injury to nerves, injured spinal cord, paralysis, and death.







